Early pregnancy scans, also known as viability scans, are typically performed between 6 and 12 weeks of gestation. They are a crucial part of prenatal care and offer valuable information about the developing fetus and the pregnancy’s progress.
Here’s a breakdown of the purposes and benefits of early pregnancy scans:
Confirmation of pregnancy:
The primary purpose of an early pregnancy scan is to confirm the presence of a pregnancy and a heartbeat. This can provide much-needed reassurance to expecting parents, especially in the early stages when pregnancy symptoms may be mild or nonexistent.
Dating the pregnancy:
By measuring the baby’s size and development, the sonographer can estimate the gestational age, or how far along the pregnancy is. This information is essential for planning future prenatal care and setting an accurate due date.
Assessing fetal viability:
The scan can detect the presence of a fetal heartbeat, which is a strong indicator of the baby’s well-being. If a heartbeat is not detected, it could be a sign of miscarriage, but further tests would be needed for confirmation.
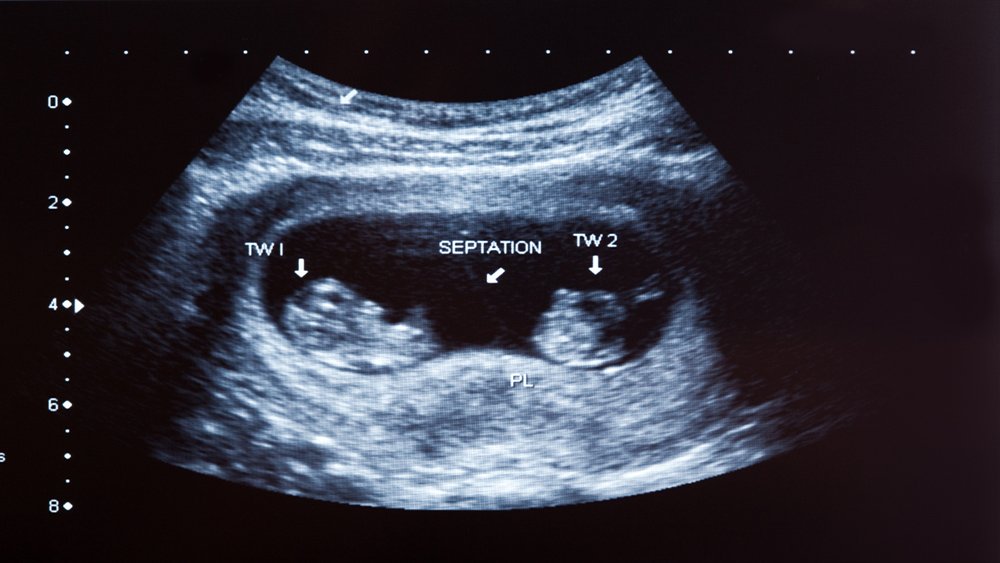
Identifying multiple pregnancies:
The scan can reveal if you are carrying twins, triplets, or more. This information is important for planning prenatal care and delivery.
Checking for certain fetal anomalies:
While not the main focus of early scans, sonographers may be able to identify some major fetal anomalies, such as neural tube defects or structural malformations. However, a more detailed scan, usually later in pregnancy, is typically recommended for a comprehensive evaluation.
Providing peace of mind:
Seeing the baby on the screen and hearing the heartbeat can be a very emotional and reassuring experience for expecting parents. It can help solidify the bond with their unborn child and alleviate anxieties about the pregnancy’s progress.
Here are some additional points to remember about early pregnancy scans:
- Early pregnancy scans are typically performed transvaginally, meaning a small probe is inserted into the vagina to get clearer images of the early pregnancy.
- The scans are painless and non-invasive, and there are no known risks associated with them.
- The information obtained from the scan should be discussed with your healthcare provider to understand its implications and make informed decisions about your prenatal care.


