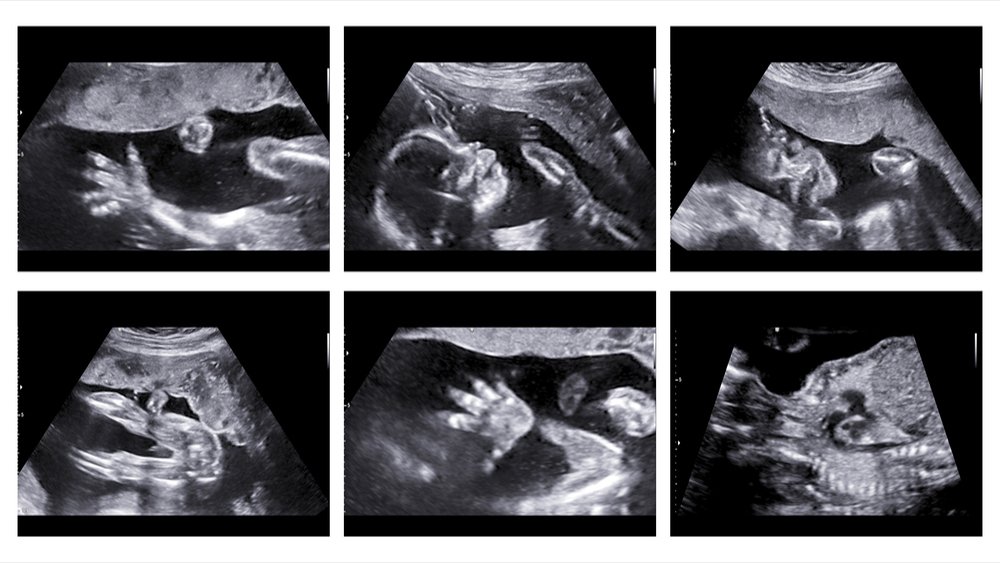
An anomaly scan, also known as a mid-trimester scan or Level II ultrasound, is a detailed prenatal ultrasound examination typically performed between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy. It is a crucial part of prenatal care, as it allows healthcare providers to assess the development of the fetus and identify any potential abnormalities.
Here’s what the anomaly scan typically involves:
- A thorough examination of the baby’s anatomy: This includes the head, face, brain, spine, heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, kidneys, bladder, limbs, and other organs.
- Measurement of the baby’s growth: This is done to ensure that the baby is developing at an appropriate rate.
- Assessment of the placenta and amniotic fluid: The placenta nourishes the baby and the amniotic fluid protects it. Checking these elements is important for ensuring the baby’s well-being.
Anomaly Scan Ultrasound
The anomaly scan can detect a wide range of potential problems, including:
- Birth defects: These are structural abnormalities that are present at birth. Some common birth defects that can be detected on an anomaly scan include heart defects, spina bifida, cleft lip and palate, and limb malformations.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: These are conditions caused by extra or missing chromosomes. Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome are some examples of chromosomal abnormalities that can be detected on an anomaly scan.
- Growth problems: If the baby is not growing at an expected rate, this could indicate a problem such as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
It is important to remember that an anomaly scan is not a diagnostic test. If a potential problem is identified on the scan, further testing, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Overall, the anomaly scan is a valuable tool that can help to identify potential problems early in pregnancy. If you have any concerns about your pregnancy, talk to your healthcare provider.


